Can Cold Sores Cause Genital Herpes? Explained
Here’s the crux of the matter. When that friend unknowingly had a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) manifesting as a cold sore, an exchange as simple as a kiss could facilitate the transmission of the virus. From there, it’s entirely possible that through oral-genital contact, what starts as a seemingly harmless cold sore can lead to genital herpes, turning a moment of intimacy into a long-term medical concern.
Understanding Cold Sores and Genital Herpes
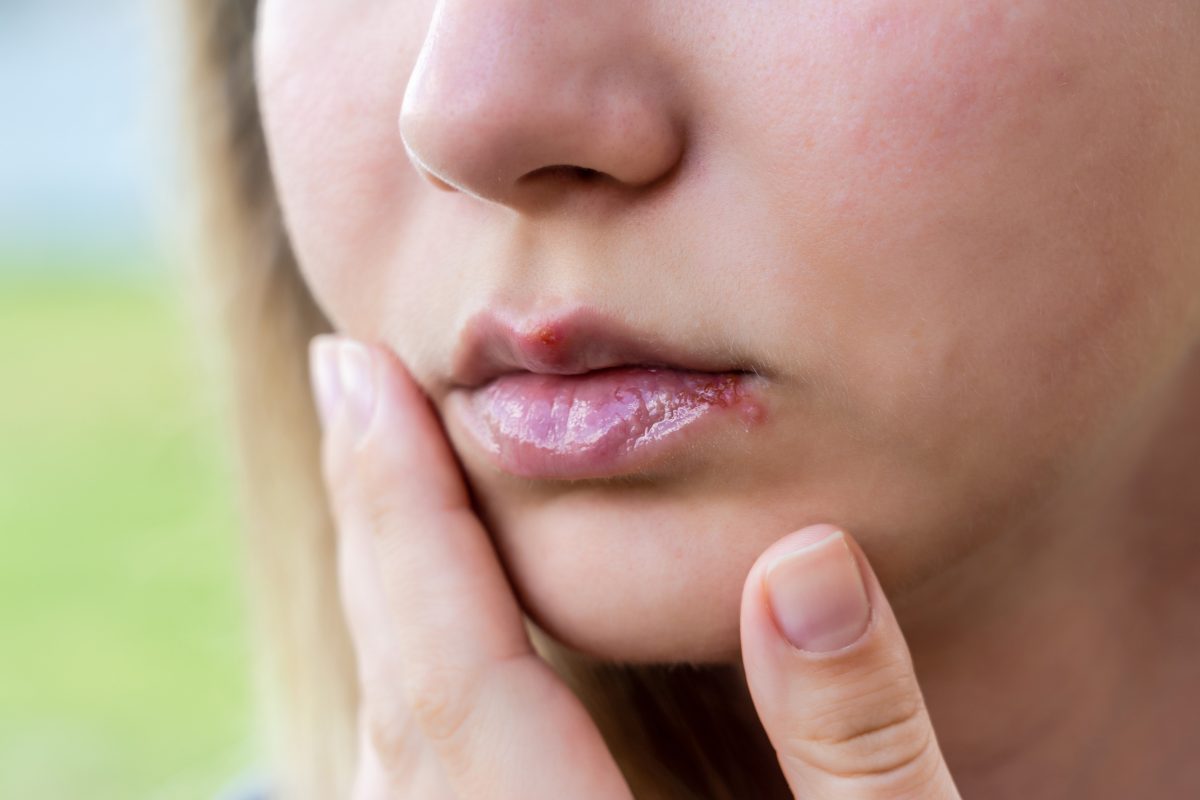
Cold sores, clinically known as herpes labialis, are superficial skin eruptions caused by the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Conversely, genital herpes is typically associated with herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), but it’s paramount to understand that HSV-1 can also lead to genital herpes through orogenital contact. This crossover is not uncommon, as HSV-1 is adept at infecting mucosal surfaces; hence, an individual with an active cold sore engaging in oral sex can transmit the virus, potentially culminating in a genital herpes infection in their partner. It is this intricacy of herpes virus transmission that necessitates meticulous attention to any existing lesions and underpins the value of reliable detection methods, such as those offered by STDCheck, to curtail the spread of this pervasive pathogen.
What Are Cold Sores?
Cold sores are lesions caused by the herpes simplex virus, prominently appearing around the mouth area. A single cold sore episode suggests lifelong HSV presence, given its dormant nature and potential reactivations. The blisters are fluid-filled and tend to cluster, often preceded by tingling, itching, or discomfort. Despite a benign appearance, cold sores harbor HSV-1, which may cross over to genital regions, proving their viral versatility.
The Genital Herpes Condition
Genital herpes, a pervasive sexual health concern, is primarily caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). However, its counterpart, herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), traditionally associated with oral lesions known as cold sores, can also be implicated in genital infections. This cross-over tends to occur through orogenital contact during an active episode of a cold sore.
In essence, genital herpes manifests through blisters in the genital area, similar to cold sores in appearance. They emerge, fraught with discomfort and potential complications for sexual health. Importantly, once the virus establishes residency in the body, it remains indefinitely, albeit occasionally dormant.
The transmission of HSV-1 to the genital region represents an atypical but significant route of infection, raising the necessity for comprehensive sexual health education. Understanding how cold sores can contribute to genital herpes underscores the importance of protective measures during sexual activity. Highlighting this potential for transmission emphasizes the need for vigilance in recognizing symptoms and seeking a diagnosis.
Within this context, utilizing the Herpes test from STDCheck becomes an indispensable tool in both identifying and mitigating the risk of spreading herpes. An accurate diagnosis is not merely about treatment—it is a vital step in preventing the further transmission of HSV. For those who engage in sexual activities, understanding that cold sores can potentiate genital herpes is an essential part of a responsible sexual health regimen. By detecting and addressing the virus, one mitigates the risks associated with this highly contagious pathology.
Connection Between HSV-1 and HSV-2
Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1) predominantly causes oral herpes but can result in genital infections through oral-genital contact. While historically separate in localization, HSV-1 and HSV-2 are now seen as fluid in their ability to infect either region.
Recent studies manifest increasing incidences of genital herpes stemming from HSV-1 transmission. This shift in epidemiology demands a reassessment of herpes transmission dynamics.
Genital herpes, traditionally associated with Herpes Simplex Virus type 2 (HSV-2), is experiencing an epidemiological transition due to the rise in oral-to-genital transmission of HSV-1. The implications of HSV-1 transitioning to genital areas include increased complications, potential for neonatal transmission, and the challenge of accurate diagnosis.
The advent of HSV-1 as a contributor to genital herpes highlights the significance of accurate testing, such as the comprehensive Herpes test offered by STDCheck. Such testing not only elucidates the type of Herpes Simplex Virus present but also supports informed decisions to prevent transmission. In recognizing the malleability of herpes viruses, individuals are empowered to take proactive steps in sexual health management, thereby lowering the risk of unknowingly facilitating the spread of the virus.
Transmission of Herpes Virus
Transmission can occur during intimate contact when herpes simplex virus is actively shedding, even without visible sores present. Specifically, cold sores caused by HSV-1 can infect genital tissue during oral sex. It is important to understand that while cold sores are often associated with the mouth and face, the same virus can establish infection in the genital region. In the absence of symptoms, herpes can still be transmitted, highlighting the role of asymptomatic viral shedding.
Employing reliable testing mechanisms, like STDCheck’s Herpes Test, is crucial for accurate herpes status awareness and preventing unwitting transmission of the virus.
Oral to Genital Transmission
HSV-1, the virus typically responsible for cold sores, can indeed be transmitted to the genital area. During oral genital contact, if a person with an active cold sore performs oral sex on a partner, the herpes virus can be transferred to the genital region, leading to genital herpes. This type of transmission is a concern because oral HSV-1 infections are quite common, and individuals may not recognize the risk during asymptomatic shedding. Asymptomatic shedding refers to the release of the herpes virus from the skin or mucous membranes even in the absence of visible sores.
Given the nuances of HSV transmission, understanding the potential risks associated with oral-genital contact is essential. Even absent any signs of an outbreak, an individual with HSV-1 can transmit the virus, underscoring the importance of protection and communication with sexual partners. This fact emphasizes the significance of informed consent and the role of medical testing in the context of sexual health.
Moreover, to curb the spread of the virus, it is imperative to undergo herpes testing to confirm one’s HSV status. STDCheck’s Herpes Test offers a confidential and accurate way to determine if an individual is carrying the virus, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding their sexual health. Early detection and knowledge of one’s herpes status are critical in mitigating the possible transfer of the virus to a partner, therefore reducing the risk of expanding the prevalence of genital herpes infections.
Risk Factors for Herpes Spread
Transmission of herpes simplex viruses, particularly from cold sores to genital regions, is influenced by several factors.
- Skin-to-skin contact: Direct touch with an infected area fosters virus spread.
- Presence of sores: The risk amplifies when cold sores are visible, though asymptomatic shedding still poses a threat.
- Immune system status: Individuals with weakened immunity are more susceptible.
- Sexual activity: Unprotected sexual encounters increase transmission likelihood.
- Mucosal membrane exposure: Oral-genital contact with an active cold sore can transmit the virus.
Engaging in oral sex with someone who has a cold sore can lead to genital herpes, even in the absence of symptoms. To limit transmission risks, practicing safe sex and regular herpes testing via services such as STDCheck’s Herpes Test is indispensable.
Protective Measures Against Transmission
Abstaining from sexual contact when cold sores are present is foundational in preventing the transference of herpes simplex viruses. For sexually active individuals, the diligent use of condoms or dental dams during all forms of sexual activity offers a substantial barrier against transmission. It’s critical to note, however, that these prophylactics may not provide complete protection if they do not cover the entire affected area. Regular communication with sexual partners about one’s herpes status and potential exposure to the virus is also a vital component of shared responsibility in reducing transmission likelihood.
Moreover, individuals should refrain from touching their own cold sores and immediately wash their hands if they do so inadvertently. This personal hygiene practice is essential in preventing the self-spread of the virus to other body parts or to others through direct contact or shared objects.
The Role of Herpes Testing in Prevention
Herpes testing is instrumental in mitigating transmission risks within sexually active populations. Through early detection, individuals can adopt precautionary measures to forestall the spread. When knowledgeable of one’s herpes status via rigorous testing, strategies such as informed consent, protected sexual encounters, and antiviral protocols can be consistently employed. This dedicated approach facilitates the reduction of viral dissemination.
Importance of Early Detection
The ability to quickly identify herpes simplex virus (HSV) infections is paramount. Gaining awareness at the earliest juncture allows for the initiation of antiviral therapies, which can decrease the intensity and duration of symptoms. Furthermore, understanding one’s own HSV status is vital for informed sexual health decisions, helping prevent the inadvertent transmission of the virus to partners.
When detected early, interventions and discussions can occur – knowledge is power. An early diagnosis enables individuals to adopt safer sex practices promptly and to communicate their status with partners, thus curtailing potential spread.
Accessing services like STDCheck’s comprehensive Herpes Test affords individuals a discreet and accurate avenue for diagnosis. Timely testing promotes proactive management of herpes, empowering individuals to navigate their sexual health with confidence and minimize the impact of the virus on their lives.
Medically Reviewed by Joshua Hwang, MD on March 21, 2024
Secure and Confidential
STD testing services
The fastest results possbile - available in 1 to 2 days

Tagged
Categorized As
Author: STD Check Editorial Team
At STDCheck.com, we go to great lengths to ensure quality content. We’re using our own collection of data. It is not bought or made up for “click-bait” purposes. We don’t entice traffic with cheesy graphics or raunchy headlines. Our information is to promote STD testing, educate people, let go of social stigmas, and bring awareness. We also provide a completely confidential atmosphere through private testing. When we produce an article, it is fact-based. We check it with medical advisors that approve it. Our staff consists of doctors and other medical professionals who peer review the content we make available on STDCheck.com. From all over the world, we have sourced the best and the brightest content developers, including medical professionals, marketing engineers, data scientists, content specialists, and media relations.