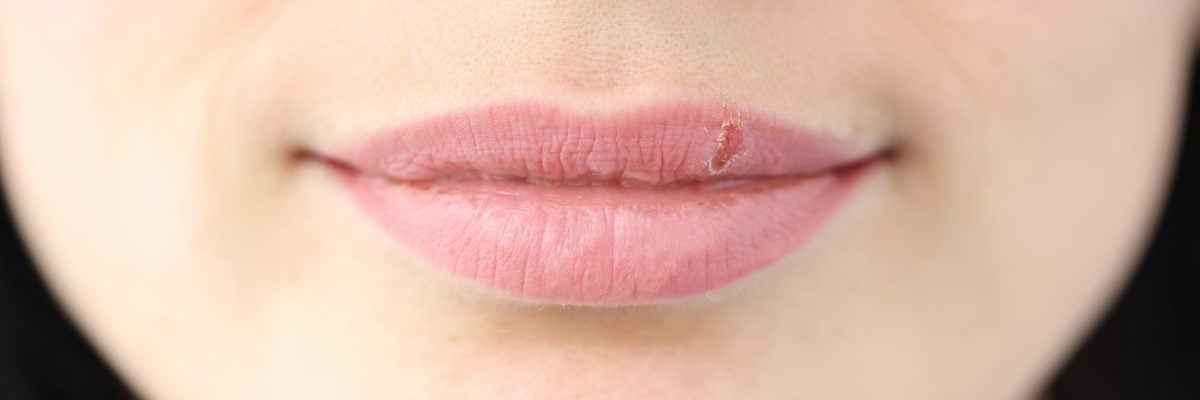
Are Canker Sores an STD?
No, canker sores are not sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). We discuss more in-depth in this article, but we want to be clear that canker sores are not STDs. While some STDs can cause sores or lesions in the genital area or mouth, canker sores are not considered to be one of them.
The link between Canker Sores and Sexually Transmitted Infections
Canker sores are a common condition that affects many people. These painful mouth sores can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, certain foods, and underlying health conditions. However, one question that often arises is whether or not canker sores are linked to sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Are canker sores an STD? We already answered the question, but in this article, we’ll explore the relationship between canker sores and STIs to help you better understand this often-misunderstood condition.
Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores, are small, painful lesions that can develop on the soft tissue inside your mouth. They are typically round or oval in shape with a white or yellow center and a red border. They can be quite painful and may make eating and talking uncomfortable. Symptoms usually include a burning or tingling sensation before the sore appears, as well as pain and tenderness around the affected area.
But what about sexually transmitted infections (STIs)? Can they cause canker sores or are they completely unrelated? Let’s explore this topic in more detail.
What Are Canker Sores?
As mentioned earlier, Canker sores, also known as aphthous ulcers or canker sores, are small, painful lesions that can develop on the soft tissue inside your mouth. They are a common condition and can affect people of all ages. They can occur singly or in clusters and may be accompanied by swollen lymph nodes or fever in severe cases.
The exact cause of canker sores is unknown, but factors such as stress, injury to the mouth (e.g., from dental work), certain foods (e.g., citrus fruits), hormonal changes, and even genetics may play a role in their development. While they are not contagious and usually go away on their own within one to two weeks, they can be quite painful and make talking and eating uncomfortable. Treatment options include over-the-counter pain relievers, topical medications, and prescription drugs for more severe cases.

STDs That Can Cause Canker Sores
Actually, there are no sexually transmitted or infections that directly cause canker sores or aphthous ulcers. However, some STIs can cause genital sores or ulcers that may be mistaken for canker sores in the mouth. These include:
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV): HSV is a common STI that causes painful blisters or sores on the genitals, mouth, and lips.
- Syphilis: Syphilis is a bacterial infection that can cause painless genital sores, as well as rashes and other symptoms.
- Chancroid: Chancroid is a bacterial infection that can cause painful genital sores.
It’s important to note that these STIs are not typically associated with canker sores in the mouth and any oral lesions should be evaluated by a doctor to determine the underlying cause. Additionally, practicing safe sex through condom use and regular STI testing can help prevent the spread of these infections.
Other Causes of Canker Sores
- Autoimmune disorders: Certain autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and Behcet’s disease, can cause oral ulcers similar to canker sores.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamin B12, folate, or iron can lead to the development of canker sores.
- Allergies: Some people may experience allergic reactions to certain foods, which can result in the formation of oral ulcers.
- Hormonal changes: Women may experience an increase in the frequency of canker sores during certain times in their menstrual cycle due to hormonal fluctuations.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), beta-blockers, and antibiotics, can cause oral ulcers as a side effect.
It’s important to note that while these conditions can cause similar symptoms to canker sores, they require different treatments and management strategies. If you are experiencing frequent or severe mouth ulcers, it is important to help and utilize a treatment plan.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for canker sores depend on the underlying cause and the severity of the symptoms. In most cases, canker sores will heal on their own within one to two weeks without any specific treatment. However, over-the-counter medications such as topical anesthetics or mouthwashes containing benzocaine or hydrogen peroxide can help relieve pain and promote healing. In severe or recurrent cases, a doctor may prescribe corticosteroids or other prescription medications to reduce inflammation and promote healing. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as reducing stress, avoiding trigger foods, maintaining good oral hygiene, and taking vitamin or mineral supplements may also help prevent or manage canker sores.
Conclusion
Canker Sore STD
It is important to note that while some sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) can cause canker sores, there are many other potential causes to consider. Canker sores can be caused by a variety of factors such as stress, hormonal changes, food allergies or sensitivities, nutritional deficiencies, and autoimmune disorders. Are canker sore STD? Nope.
Medically Reviewed by Kaci Durbin, MD, MBA, FACOG on February 20, 2023
Secure and Confidential
STD testing services
The fastest results possbile - available in 1 to 2 days

Tagged
Categorized As
Author: STD Check Editorial Team
At STDCheck.com, we go to great lengths to ensure quality content. We’re using our own collection of data. It is not bought or made up for “click-bait” purposes. We don’t entice traffic with cheesy graphics or raunchy headlines. Our information is to promote STD testing, educate people, let go of social stigmas, and bring awareness. We also provide a completely confidential atmosphere through private testing. When we produce an article, it is fact-based. We check it with medical advisors that approve it. Our staff consists of doctors and other medical professionals who peer review the content we make available on STDCheck.com. From all over the world, we have sourced the best and the brightest content developers, including medical professionals, marketing engineers, data scientists, content specialists, and media relations.